Likes
The Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, commonly referred to as the “Third Pole,” is undergoing significant environmental changes. Its alpine wetlands, crucial for regional biodiversity and water regulation, exhibit signs of distress, including diminishing water resources and degradation of meadows. However, persistent cloud and snow cover complicate consistent, long-term monitoring of these ecosystems. Researchers from South China Normal University, Tibet University, and the Chinese Academy of Sciences have created a new tool to tackle this issue.
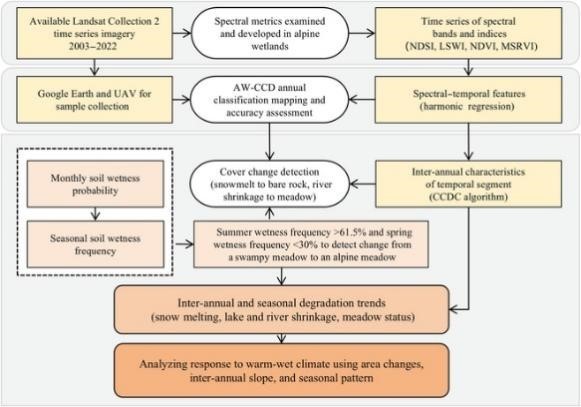
Published in the January 2, 2025, issue of the Journal of Remote Sensing, the Alpine Wetlands Change Detection (AW-CCD) algorithm uses Landsat time series data to monitor ecosystem changes on the cloud-covered Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. The framework aims to classify wetlands annually and track degradation by integrating long-term inter-annual data with seasonal soil moisture indicators. This method improves snow cover detection by 5% and meadow classification by 3%, achieving a mapping accuracy of 94.9% in the Maidika Wetland in 2022.
The study reveals significant environmental shifts over the past two decades. Snow and river areas in the Maidika Wetland decreased by 5.04% and 16.74%, respectively, while 3.23% of swampy meadows transitioned into drier alpine meadows. The most severe degradation occurred before 2009, followed by a stabilization period until 2015 and a resurgence in recent years. To capture these changes, the AW-CCD algorithm uses spectral-temporal index features, such as the Normalized Difference Snow Index (NDSI) for snow detection and the Meadow Spectral Ratio Vegetation Index (MSRVI) for differentiating meadow wetness.
The research team analyzed Landsat images from 2003 to 2022, using the Fmask algorithm to minimize cloud and shadow disruptions. Elevation and slope data from the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission, ALOS World 3D-30m, and Global Surface Water data further enhanced classification accuracy.
Source: https://url.scnu.edu.cn/record/view/index.html?key=e2c206d6bde053e2fcf395057cf53c08
The source URL for this press release: New Algorithm Reveals Critical Alpine Wetland Degradation in the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau
What to read next:










