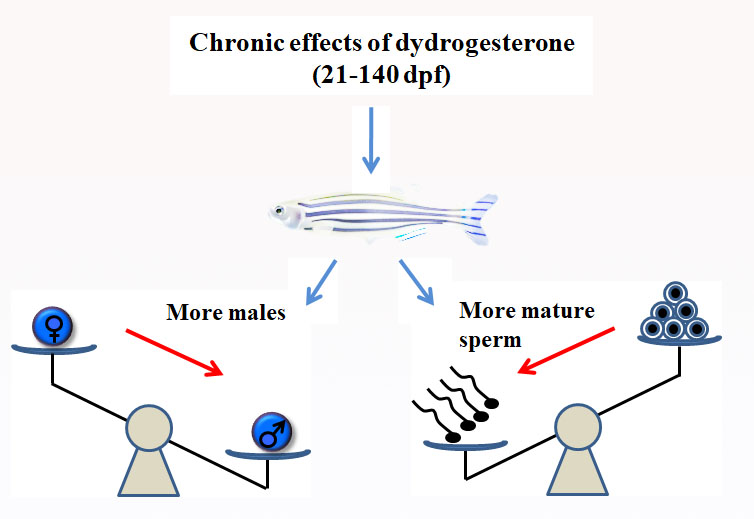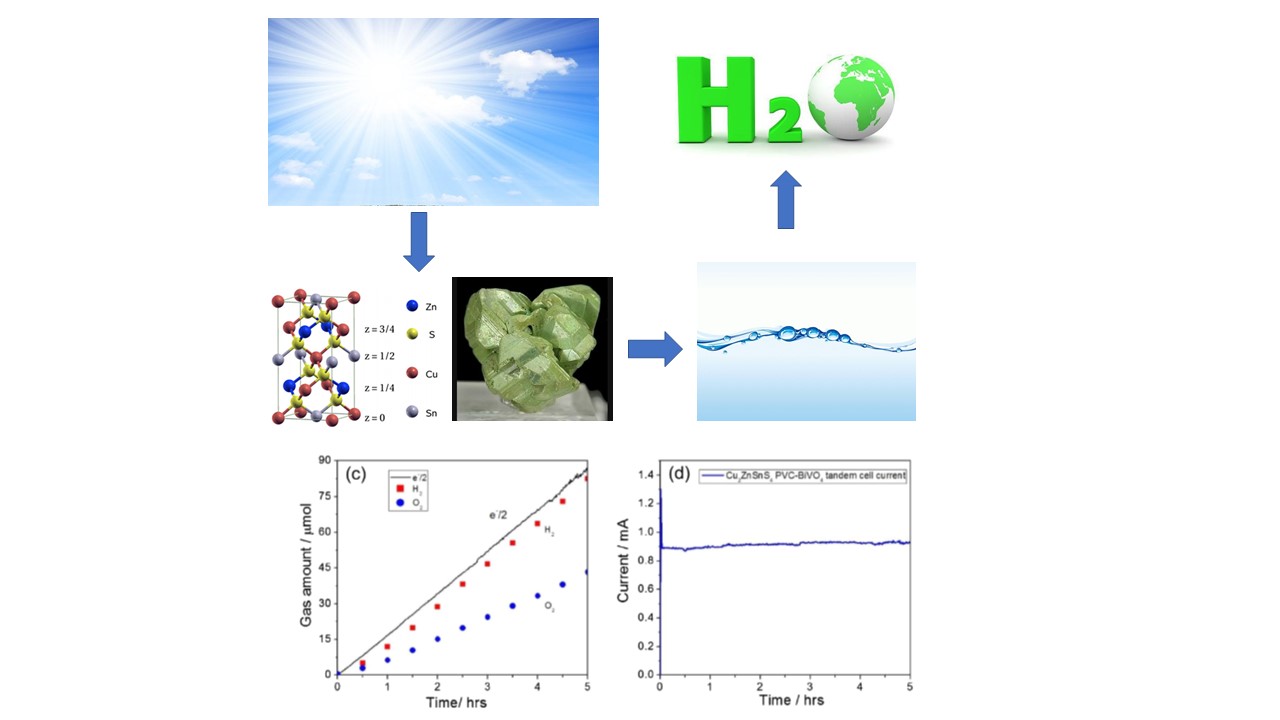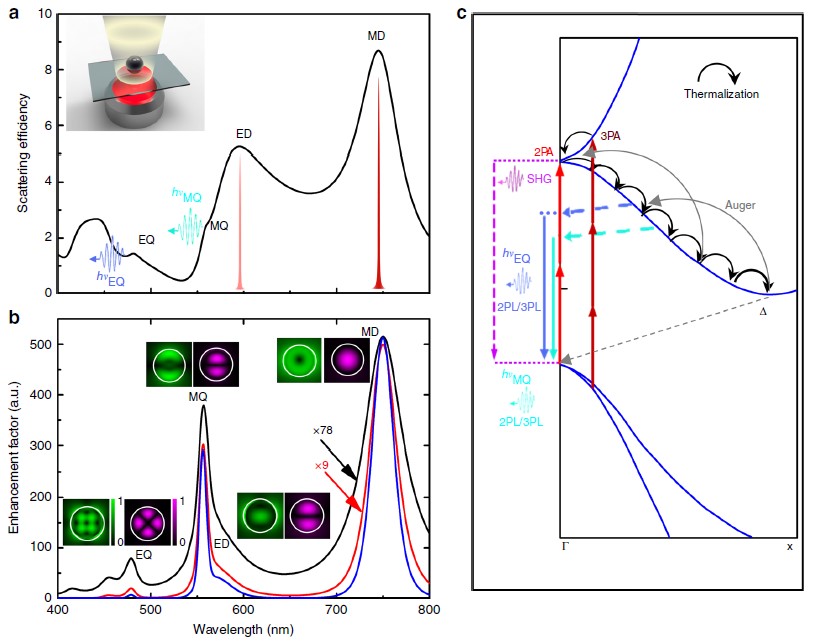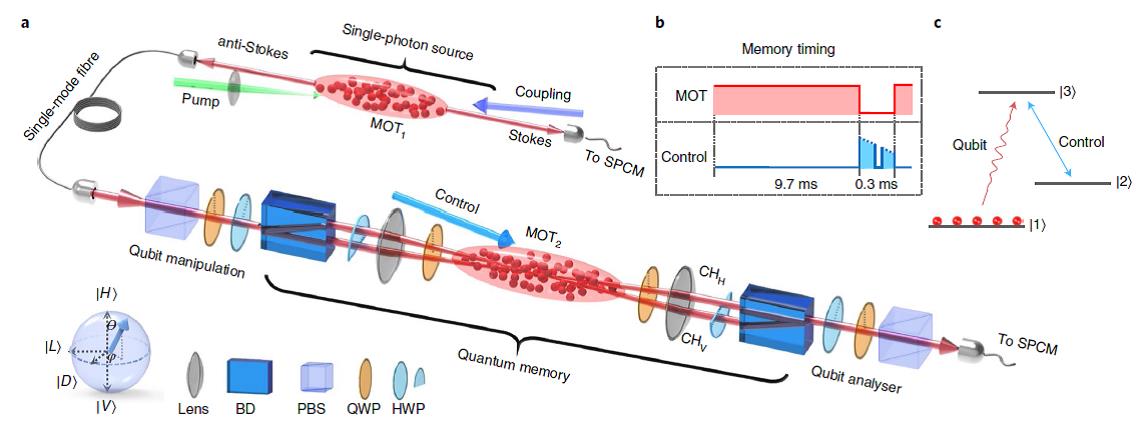
Likes
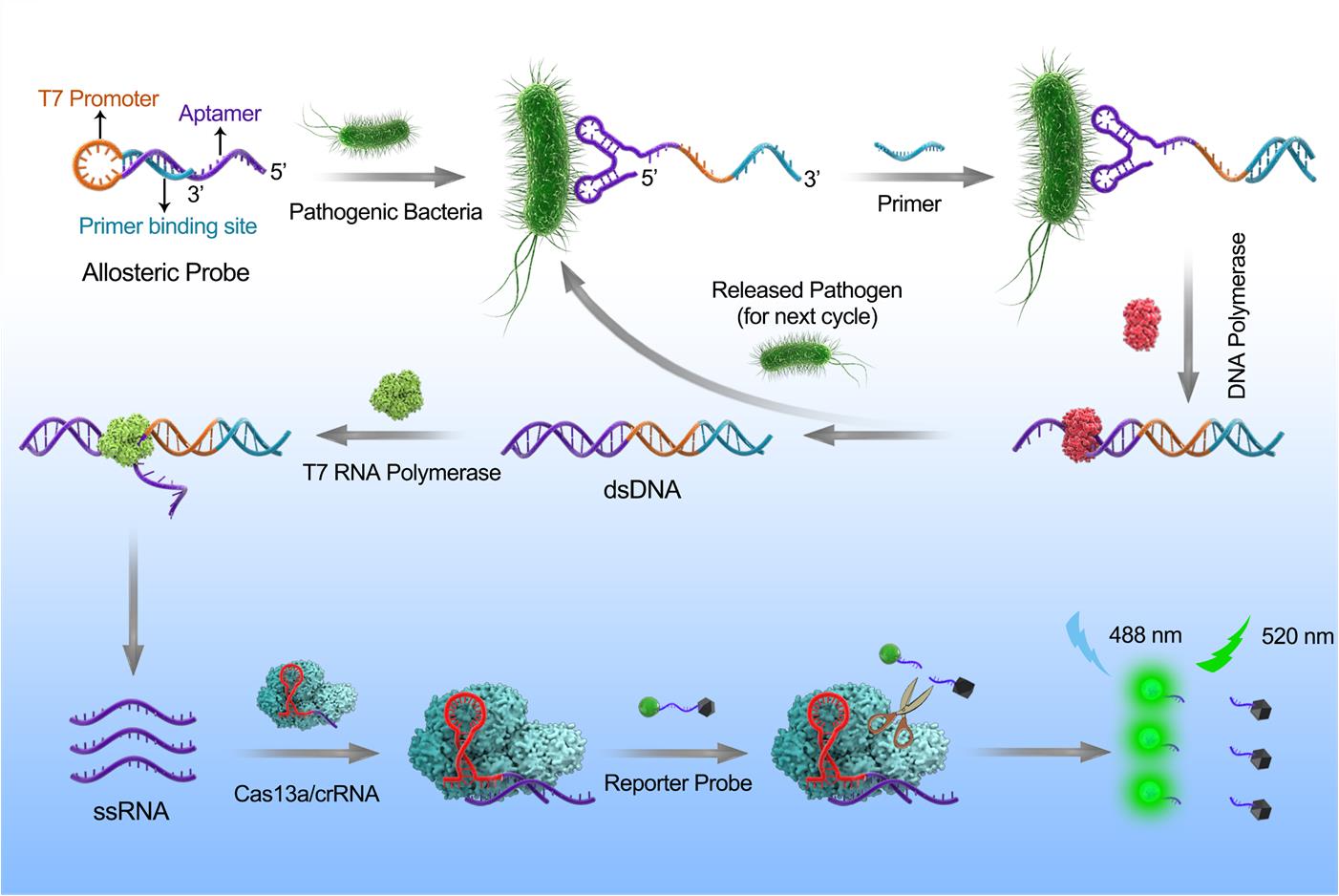
A research paper entitled Sensitive detection of a bacterial pathogen using allosteric probe-initiated catalysis and CRISPR-Cas13a amplification reaction was published in Nature Communications by Professor Xing Da's team of the College of Biophotonics, the MOE Key Laboratory of Laser Life Science & Institute of Laser Life Science, South China Normal University, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory. This article presents a detection system (called ‘APC-Cas’) that can detect very low numbers of a bacterial pathogen without isolation, using a three-stage amplification to generate powerful fluorescence signals. APC-Cas involves a combination of nucleic acid-based allosteric probes and CRISPR-Cas13a components.

The research team used aptamers to construct an allosteric DNA molecule that can bind to a target pathogen and convert it into its active configuration. In its active configuration, the catalytic pathogen binds to aptamers (primary amplification), triggers isothermal amplification (secondary amplification), and activates the trans-cutting activity CRISPR / Cas13a (tertiary amplification), which amplifies the fluorescent signal by cutting RNA report probes, the cascade three-stage amplification produces detectable fluorescence signals, enabling direct detection of pathogens without the needs for isolation or extraction of nucleic acids. In addition, the team demonstrated greater sensitivity, accuracy, and ease of operation with APC-Cas compared to traditional real-time PCR methods through methodological comparisons, it indicates that APC-Cas has potential clinical value in the diagnosis of bacterial diseases.

The team has been working in recent years to develop CRISPR technology for Molecular Diagnostics, by designing functional molecules of nucleic acids that can be used to identify and detect tumor-related MicroRNAs and pathogenic microbes, combining the specific recognition ability of CRISPR proteins, a variety of CRISPR molecular diagnostic techniques have been developed to provide technical support for early detection of tumors and rapid detection of pathogens.
The lead author is Shen Jinjin, a postgraduate student at the College of Biophotonics of South China Normal University, and professors Hu Jiaming and Xing Da are co-corresponding authors of the paper. This work has been supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province.
Paper Link:
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-019-14135-9
Translated by Li Xinyi
Proofread by Edwin Baak
Reviewed by Li Jianru
What to read next: