Likes
Recently, the "Young Talent" of South China Normal University (SCNU) researcher Jiang Feng and his research group published a series of important research findings in the American Chemical Society's authoritative journal "ACS Energy Letters" (Impact Factor 12.277) and the "Solar RRL" of "Advanced Materials". SCNU is listed as the sole contact/ first unit.

Important research findings were shown in the journal
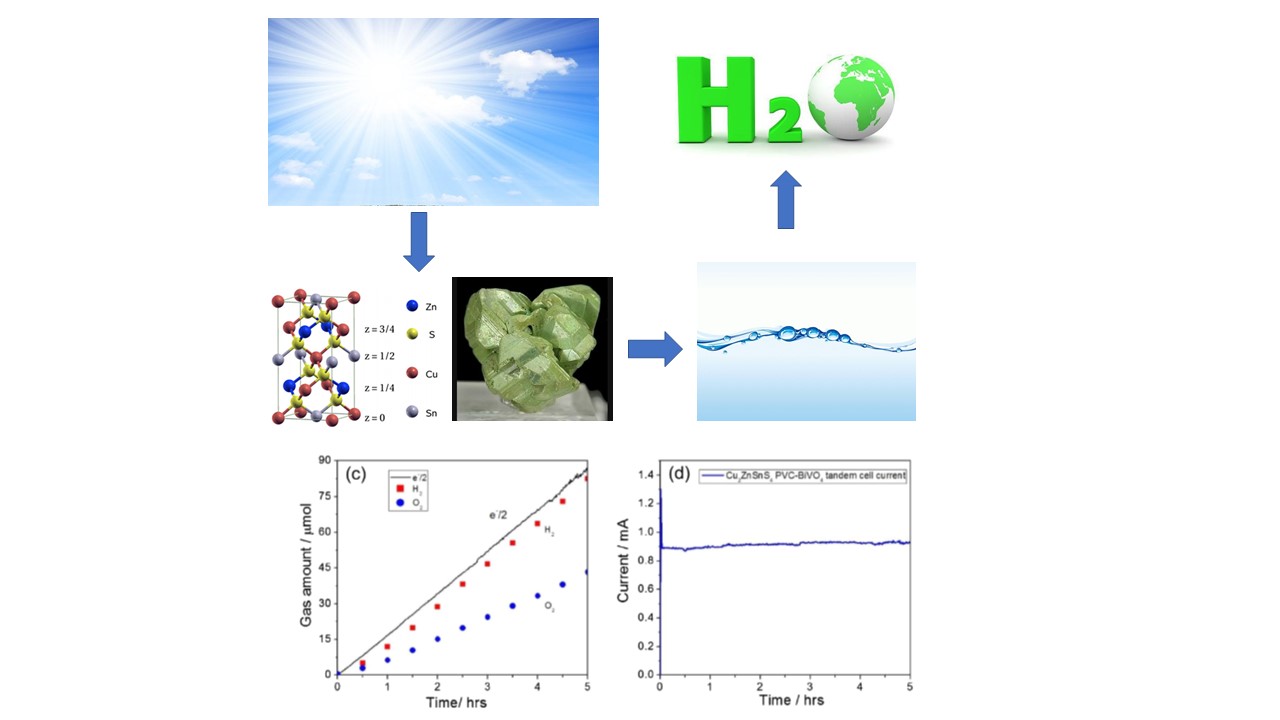
Low-cost, environmentally-friendly, efficient and stable solar hydrogen production technology is the most ideal way to convert and utilize solar energy. A Cu2ZnSnS4 (CZTS) is generally considered to be an ideal solar hydrogen electrode material due to its low-cost, non-toxic and environmentally friendly components, with an optical band gap close to 1.5 eV. The research team of Jiang Feng conducted an in-depth research on the influence mechanism of the interface state and performance change of CZTS on the photoelectric characteristics of the photoelectrode cathode by means of in-situ deposition and surface passivation modification. They made a breakthrough in the hydrogen production efficiency from CZTS photoelectrode decomposition of water and greatly expanded the light stability of the device. In combination with the photoanode, the world's highest efficiency of CZTS unbiased decomposition of water to produce hydrogen is thus achieved.
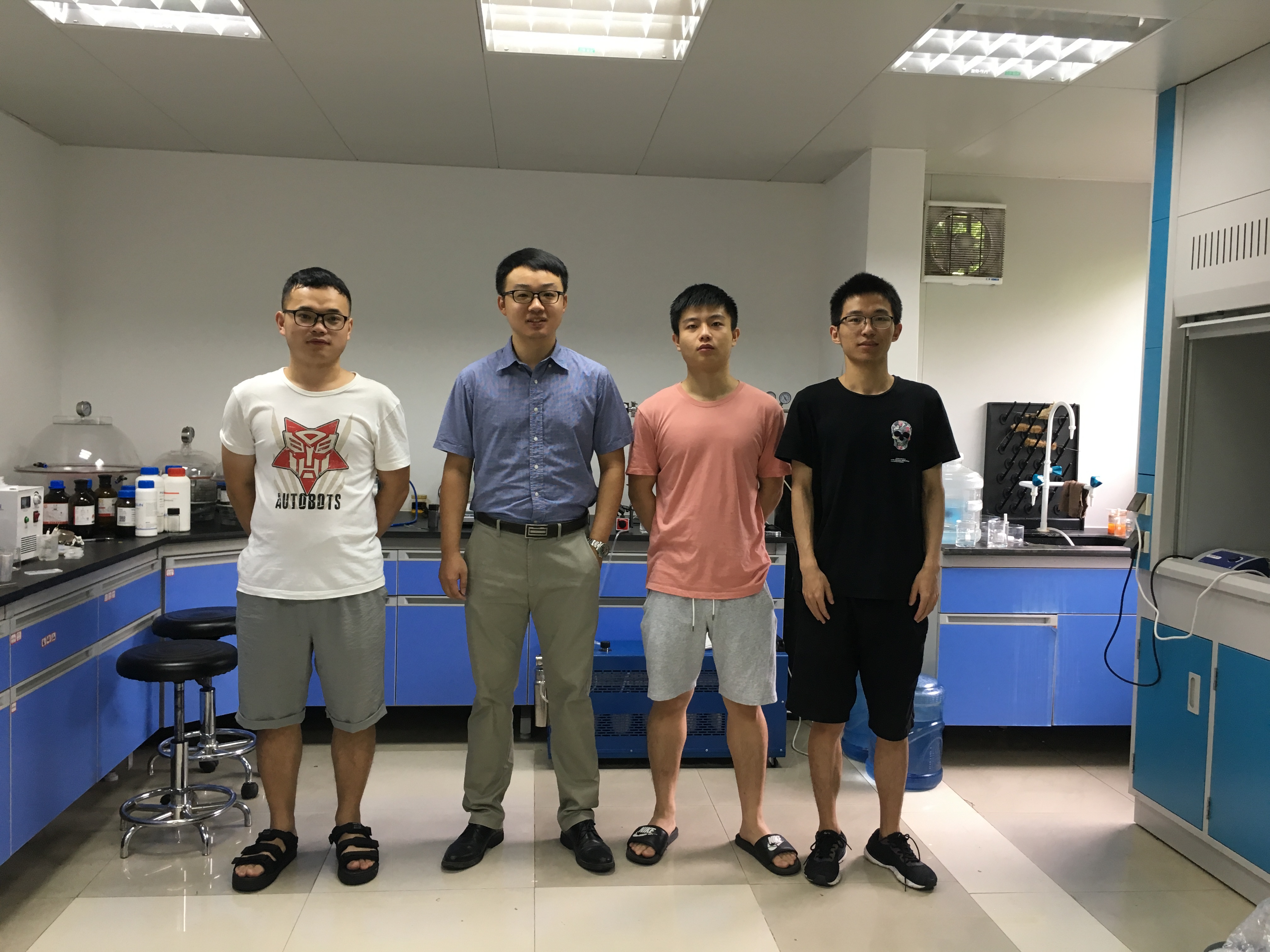

Group photo of the Research group
Huang Dingwang, a SCNU postgraduate student of 2017, is the first author of the article. Wang Kang and Yu Le, both postgraduate students of 2017 as well, are the co-authors of the paper. The researcher Jiang Feng is the corresponding author of the paper. This is the first time that SCNU has published a paper in ACS “Energy Letters”.
Source from Institute of Optoelectronic Materials and Technology
Translated by Li Jianru
Proofread by Edwin Baak
What to read next: